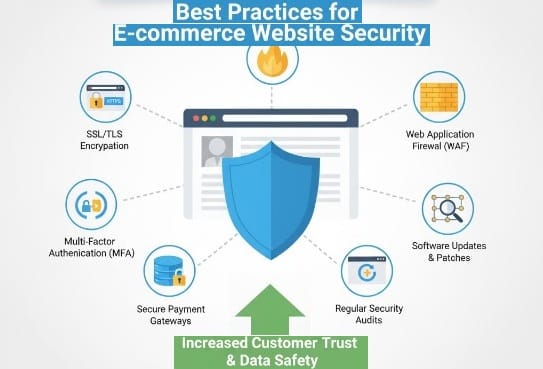
Introduction: Why E-commerce Security Is Non-Negotiable
Imagine this: a customer visits your online store, adds items to the cart, and enters their credit card details — only to discover later that their information was stolen. Not only have you lost a sale, but your brand reputation is damaged permanently.
In 2025, website security is no longer optional. With cyber threats evolving rapidly, even small e-commerce stores can become targets. Protecting your website builds trust, protects customers, and ensures smooth operations.
This guide will show you best practices for e-commerce website security, helping you safeguard your business while keeping customers confident.
1. Use HTTPS and SSL Certificates
HTTPS ensures that data between your website and visitors is encrypted.
- SSL Certificates are essential for secure transactions
- Display a padlock icon in the browser to build trust
- Google prioritizes HTTPS sites in search rankings
Example:
A small online clothing store switched from HTTP to HTTPS. Besides increasing trust, bounce rates dropped as visitors felt safer entering payment info.
Pro Tip: Most website platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce provide free SSL certificates — always enable them.
2. Keep Software and Plugins Updated
Outdated software is one of the most common security vulnerabilities.
- Regularly update your CMS, plugins, themes, and apps
- Remove unused plugins to minimize attack points
- Use platform-provided updates rather than ignoring notifications
Example:
An e-commerce store running an outdated WooCommerce plugin experienced a data breach. After updating, they implemented a routine schedule and avoided future attacks.
3. Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Weak passwords make it easy for hackers to access your admin panel.
- Use unique, complex passwords for all accounts
- Implement MFA for admins and critical accounts
- Consider a password manager for secure storage
Pro Tip: Change passwords periodically and avoid using the same password across platforms.
4. Secure Your Payment Processing
Payment security is critical for both trust and compliance.
- Use PCI-compliant payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, or Square
- Avoid storing sensitive credit card data on your server
- Monitor transactions for suspicious activity
Example:
A small electronics store switched to a PCI-compliant gateway and added automatic fraud detection tools. Chargebacks decreased by 40%, and customers felt safer completing purchases.
5. Protect Customer Data
Your customers’ personal information is invaluable and must be safeguarded:
- Encrypt sensitive data (emails, addresses, phone numbers)
- Limit access to internal teams
- Create a data privacy policy to communicate security practices
Pro Tip: Implement role-based access controls — not everyone in your team needs admin-level permissions.
6. Use Firewalls and Anti-Malware Tools
Firewalls and malware scanners add extra layers of protection:
- Web Application Firewall (WAF) blocks suspicious traffic
- Anti-malware plugins scan for viruses and malicious scripts
- Regularly schedule scans and monitor alerts
Example:
A small fashion boutique implemented a WAF and detected an attempted SQL injection, preventing a potential breach.
7. Backup Your Website Regularly
Even the most secure websites can face accidental data loss or attacks.
- Schedule automatic backups daily or weekly
- Store backups offsite or in the cloud
- Test your backups periodically to ensure recovery works
Pro Tip: Platforms like Shopify automatically backup, but WooCommerce or custom setups need plugin-based solutions like UpdraftPlus.
8. Educate Your Team About Cybersecurity
Human error is often the weakest link.
- Train staff to recognize phishing emails
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi for admin logins
- Limit access to sensitive information
Example:
A small electronics retailer lost admin access after an employee fell for a phishing email. After training, similar incidents dropped to zero.
9. Monitor Your Site Continuously
Security isn’t a one-time setup.
- Use monitoring tools to detect downtime or unusual activity
- Enable alerts for multiple failed login attempts
- Regularly check error logs and traffic analytics
Pro Tip: Tools like Sucuri, Cloudflare, or Wordfence can provide comprehensive monitoring for small e-commerce stores.
10. Implement a Clear Security Policy
Communicating security measures boosts customer confidence:
- Publish a privacy policy and terms of service
- Display security badges on checkout pages
- Mention encryption, secure payments, and data protection practices
Example:
A small home goods store added a “Secure Checkout” badge, SSL padlock, and privacy notice. Conversion rates improved by 15% because customers felt safe entering payment details.
Conclusion: Security Protects Your Business and Your Customers
E-commerce success depends not only on traffic and sales but also on trust and reliability. By implementing these best practices, you can protect your online store from cyber threats, safeguard customer data, and enhance your brand reputation.
🔑 Interactive Question: Which area of your e-commerce security needs the most attention — payments, data protection, or website monitoring?
CTA: Review your website today, implement at least three of these security practices, and ensure your customers feel safe shopping with you.